Introduction to the Low Residue Diet
Navigating the world of diets can feel overwhelming, especially with so many options available. Among them, the low residue diet stands out for its unique approach to digestive health. This dietary plan is not just a trend; it serves a specific purpose that many people find beneficial. Whether you’re managing gastrointestinal issues or preparing for medical procedures, understanding what this diet entails can be crucial. Join us as we delve into the ins and outs of a low residue diet—its benefits, food choices, and practical tips to make your journey smoother and more enjoyable!
What is a Low Residue Diet and Who Can Benefit from It?
A low residue diet focuses on reducing the amount of undigested food that passes through the intestines. This eating plan limits high-fiber foods, making it easier for your digestive system to process everything.
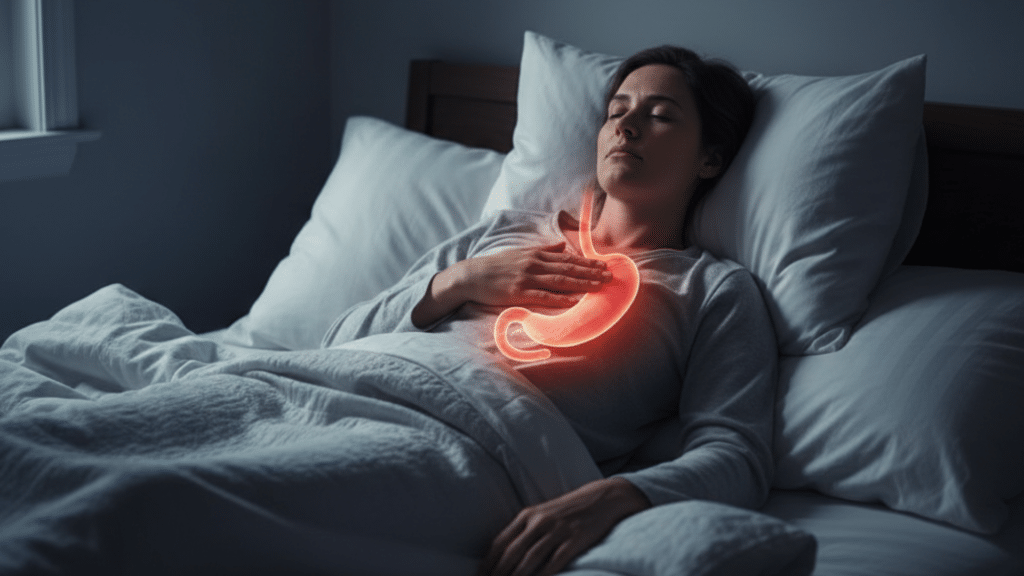
People often turn to this diet before surgeries or certain medical procedures, especially those involving the gastrointestinal tract. It can also be beneficial for individuals experiencing flare-ups of inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn’s or ulcerative colitis.
This approach helps minimize discomfort and promotes healing by allowing the gut to rest. Patients with diverticulitis may find relief as well since fewer residues ease pressure in the colon.
It’s vital for anyone considering this dietary change to consult a healthcare professional first. Personalized guidance ensures you meet nutritional needs while reaping maximum benefits from a low residue diet.
The Benefits of a Low Residue Diet
The low residue diet offers several key benefits, especially for those with gastrointestinal issues. By reducing the amount of fiber and undigested food in your digestive tract, it can help minimize symptoms like bloating and gas.
For individuals recovering from surgery or managing inflammatory bowel diseases, this diet provides a gentle approach to healing. It allows the digestive system to rest while still supplying essential nutrients.
Many people also find that a low residue diet helps them identify food sensitivities. With fewer foods on the plate, it’s easier to pinpoint which items may trigger discomfort.
Additionally, this dietary plan can promote better nutrient absorption. With less bulk in the intestines, your body might more effectively utilize vitamins and minerals from what you do eat.
Foods to Eat on a Low Residue Diet
When following a low residue diet, choosing the right foods is essential for managing digestive health. Focus on easily digestible options that provide the necessary nutrients without adding extra bulk to your stool.
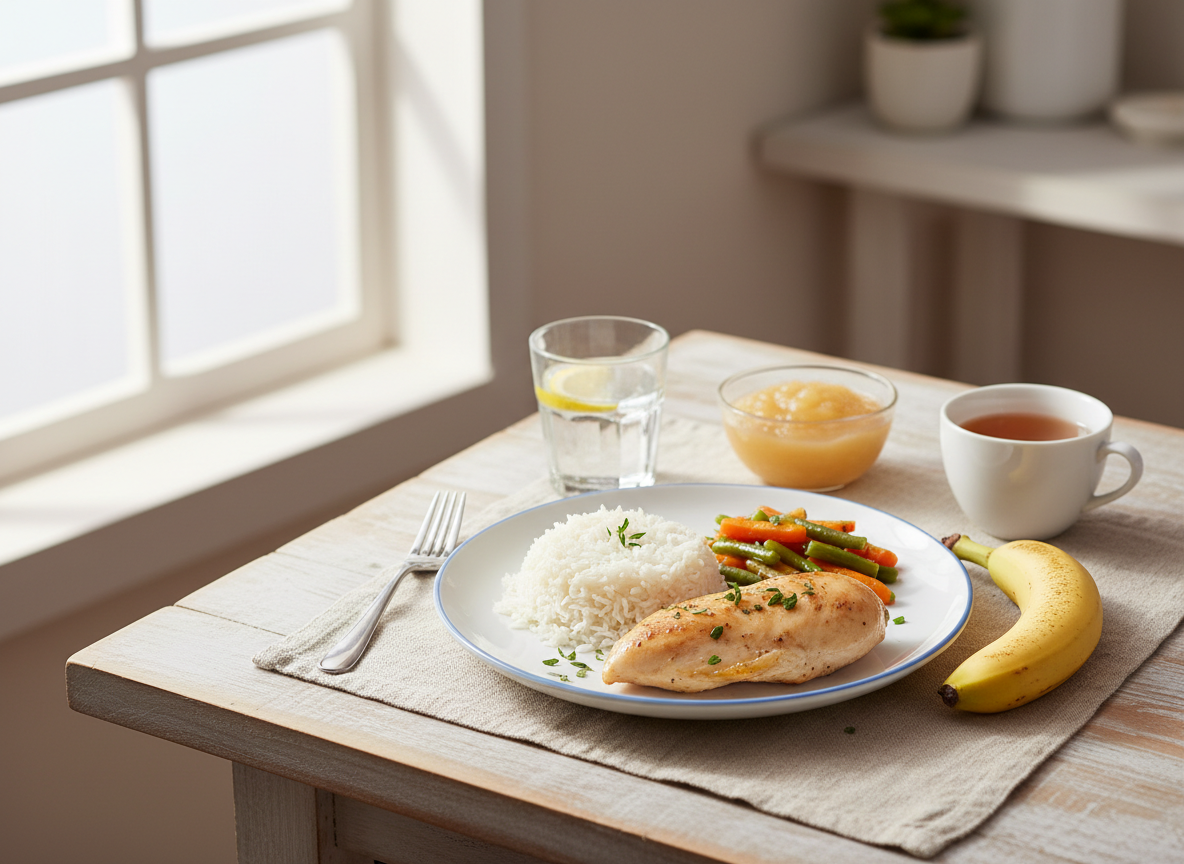
White bread and refined cereals are great choices. They offer carbohydrates with minimal fiber content. You can enjoy plain pasta or rice as well for a filling base in meals.
Lean proteins like chicken, turkey, and fish are ideal. Eggs also make an excellent protein-rich option that’s gentle on the stomach.
Fruits should be limited to those without skins or seeds. Applesauce and ripe bananas fit perfectly into this category, providing some natural sweetness without overwhelming your digestive system.
Don’t forget about well-cooked vegetables such as carrots or zucchini. These can add flavor and nutrition while remaining easy to digest when prepared correctly.
Foods to Avoid on a Low Residue Diet
When following a low residue diet, it’s crucial to steer clear of foods that can irritate the digestive system. High-fiber items are typically at the top of this list. Whole grains, legumes, and raw fruits and vegetables should be avoided.
Nuts and seeds also fall into this category. Their coarse texture can make digestion difficult for those needing a gentler approach.
Dairy products may cause discomfort too, especially if lactose intolerant. Creamy sauces or full-fat cheese should be limited as well.
Certain meats like tough cuts or processed varieties may not sit well either. Opting for lean meats is a better choice when you must include protein in your meals.
Additionally, stay away from spicy foods and caffeinated beverages which could exacerbate symptoms rather than soothe them. Keeping these guidelines in mind will help maintain comfort while navigating dietary restrictions.
Meal Ideas and Recipes for a Low Residue Diet
When planning meals on a low residue diet, simplicity is key. Start your day with creamy oatmeal made from refined grains, topped with a drizzle of honey. Pair it with yogurt for added protein.
For lunch, consider a smooth chicken or turkey sandwich on white bread. Add just a hint of mayonnaise and skip the crunchy veggies to keep it gentle on the digestive system.
Dinner can be flavorful yet mild. Try baked salmon seasoned lightly with herbs, served alongside mashed potatoes or well-cooked rice. Steamed carrots are a great side choice; they provide nutrition without adding too much bulk.
Snacks can include soft cheeses or cottage cheese paired with applesauce. For something sweet, opt for pudding or custard that satisfies cravings while remaining compliant with dietary needs.
Experimenting within these parameters can lead to enjoyable and satisfying meals throughout your low residue journey.
Tips for Successfully Following a Low Residue Diet
Sticking to a low residue diet can be simple with some practical tips. Start by planning your meals ahead of time. This helps prevent last-minute decisions that might lead you off track.
Keep a food journal. Writing down what you eat can help identify foods that work well for you and those that don’t.
Stay hydrated, but choose clear liquids wisely. Aim for water, broth, or clear juices while avoiding heavy beverages like smoothies or whole fruit juices.
When dining out, don’t hesitate to ask questions about menu options. Many restaurants are willing to accommodate dietary needs if requested politely.
Surround yourself with support. Engage friends or family members who understand your goals and can provide encouragement along the way.
Conclusion
Adopting a Low Residue Diet can be a significant step toward better digestive health. By understanding the principles of this dietary approach, individuals can make informed choices that suit their specific needs. Whether you’re preparing for medical procedures or managing certain gastrointestinal conditions, knowing which foods to embrace and which ones to avoid is essential.
The benefits are clear—from reducing symptoms of discomfort to promoting healing in the gut. With carefully selected meal ideas and creative recipes at your disposal, following this diet doesn’t have to be bland or limiting. It allows you to savor flavors while keeping your digestive system calm.
Navigating through food options may seem daunting at first, but with planning and preparation, it becomes easier over time. Embracing tips for success will help maintain adherence while ensuring nutritional needs are met.
A well-rounded approach not only alleviates symptoms but also empowers people on their journey towards optimal health. So if you’ve been considering a Low Residue Diet, now might just be the right time to explore its potential benefits for you.