Understanding Wearable Medical Devices for Remote Health Monitoring
The global wearable medical devices market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with projections indicating it will reach $185 billion by 2030, driven by an aging population and rising healthcare costs. Wearable health monitoring devices have transformed from simple fitness trackers into sophisticated medical-grade instruments capable of continuous patient surveillance outside traditional clinical settings.
These devices encompass everything from smartwatches that monitor heart rhythms to advanced smart patches that track glucose levels and medication adherence. What makes them revolutionary isn’t just their convenience—it’s their ability to capture real-time physiological data that was previously only available through hospital equipment or periodic doctor visits.
Remote health monitoring represents a fundamental shift in healthcare delivery. Instead of reactive treatment based on periodic checkups, healthcare providers can now access continuous streams of patient data, enabling proactive interventions and personalized treatment plans. A common pattern is early detection of health deteriorations that might otherwise go unnoticed until emergency situations arise.
However, this technological advancement comes with important considerations around data privacy, device accuracy, and integration with existing healthcare systems. Understanding these various types of monitoring devices and their specific applications is crucial for making informed decisions about personal health management.
Types of Wearable Medical Devices
The landscape of remote health monitoring wearables has evolved into distinct categories, each serving specific healthcare needs and patient populations. Fitness trackers represent the most consumer-accessible option, monitoring basic metrics like steps, heart rate, and sleep patterns. These devices have become the gateway for millions to engage with their health data daily. Smartwatches have emerged as comprehensive health platforms, integrating features like ECG monitoring, blood oxygen sensing, and fall detection. Apple Watch and Samsung Galaxy Watch models now offer FDA-approved capabilities that can detect irregular heart rhythms and automatically alert emergency services. Medical-grade wearables represent the clinical tier, including continuous glucose monitors, cardiac event monitors, and specialized devices for chronic disease management. These professional-grade devices often require prescription and provide hospital-quality monitoring in home settings. Smart clothing and patches constitute the emerging frontier, embedding sensors directly into textiles or adhesive monitoring patches. These innovations promise seamless integration into daily life without the need for separate devices.
The diversity in remote health monitoring wearables ensures options for every healthcare scenario, from wellness tracking to critical patient monitoring.
How Do Wearable Health Devices Work?
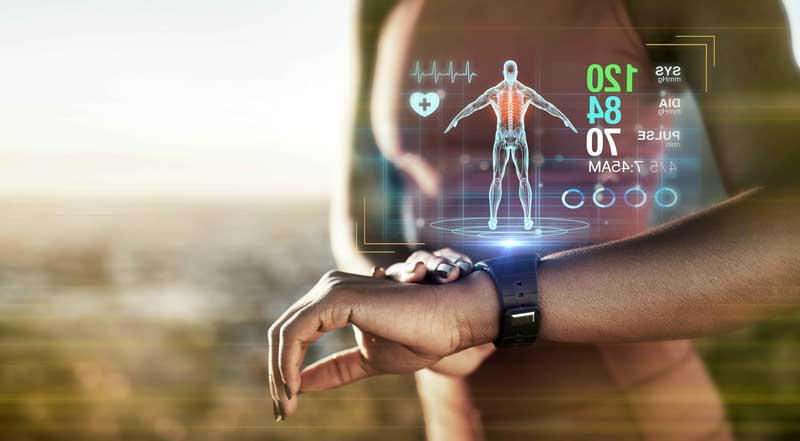
Wearable medical devices operate through a sophisticated combination of sensors, data processing algorithms, and wireless connectivity to continuously monitor physiological parameters. At their core, these devices employ various types of sensors—including optical sensors for heart rate monitoring, accelerometers for motion detection, and electrochemical sensors for glucose measurement—that collect real-time biological data from the user’s body.
The magic happens in the data processing layer, where advanced algorithms analyze raw sensor readings and convert them into meaningful health metrics. For instance, photoplethysmography (PPG) sensors use light to detect blood volume changes, while machine learning algorithms interpret these patterns to calculate heart rate variability and detect irregular rhythms.
Connectivity and cloud integration represent the final crucial component. Most devices transmit data via Bluetooth to smartphone apps, which then sync with cloud-based platforms for storage and analysis. This architecture enables healthcare providers to access patient data remotely and set up automated alerts for concerning trends.
According to Mordor Intelligence, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities is enhancing these devices’ predictive accuracy, making them more valuable for preventive healthcare approaches.
The seamless integration of hardware sensors, intelligent software, and wireless communication creates a comprehensive monitoring ecosystem that transforms how we approach personal health management.